- Sudafed (pseudoephedrine) is best for nasal congestion but can cause side effects like increased heart rate and high blood pressure.
- Mucinex (guaifenesin) is effective for chest congestion but may not address nasal symptoms.
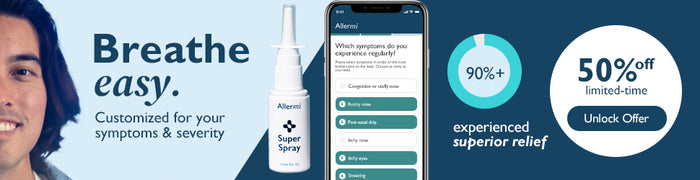
- Allermi is a customized nasal spray that provides faster relief (within 10-15 minutes) and lasts longer (3-4 weeks). It also has fewer side effects.
When faced with the discomfort of respiratory symptoms like nasal congestion or chest congestion, many people turn to Sudafed or Mucinex for relief. These two popular over-the-counter medications are usually found side by side on pharmacy shelves, but they serve different purposes.
Imagine waking up with a stuffy nose and a persistent cough — how do you decide which medication to take? Here’s what you need to know about the key differences between Sudafed and Mucinex.
We’ll also share the best alternative to manage respiratory discomfort.
Related: What to Do When Allergy Medicine Doesn't Work?
What is Sudafed?
Sudafed is a widely used over-the-counter medication that helps relieve nasal congestion caused by the common cold, sinusitis, hay fever, and other respiratory allergies. Its primary active ingredient, pseudoephedrine, is a potent decongestant that works by narrowing the blood vessels in the nasal passages. This reduces swelling and makes it easier to breathe [*].
Some Sudafed products contain phenylephrine instead of pseudoephedrine. Phenylephrine also acts as a decongestant, though it is generally considered less effective than pseudoephedrine.
Important note: To prevent the misuse of pseudoephedrine in making methamphetamine, the Combat Methamphetamine Epidemic Act of 2005 requires these products to be kept behind the pharmacy counter. Buyers must show ID, provide personal information, and follow state-specific purchase limits.
What is Mucinex?
Mucinex is a widely used over-the-counter medication formulated to relieve chest congestion associated with colds, respiratory infections, or allergies.
Its active ingredient, guaifenesin, is an expectorant that helps thin and loosen mucus in the airways. This makes it easier to cough up mucus to clear the lungs and reduce chest tightness for improved breathing [*].
Mucinex comes in various forms, including immediate-release and extended-release tablets, liquids, and sachets, catering to different needs and preferences.
In addition to guaifenesin, some Mucinex formulations include other active ingredients. For example, products containing dextromethorphan provide cough suppression by reducing the brain's cough reflex.
Sudafed vs. Mucinex
If you're unsure whether to choose Sudafed or Mucinex for your symptoms, the table below breaks down how each medication works, their side effects, and other important details.
| Sudafed | Mucinex | |
| Drug Class | Decongestant | Expectorant |
| Generic Name | Pseudoephedrine | Guaifenesin |
| Indications | Sudafed is primarily used to relieve nasal and sinus congestion caused by conditions such as the common cold, allergies, hay fever, or sinusitis. Additionally, Sudafed can help alleviate ear congestion associated with colds or air travel by relieving pressure in the Eustachian tubes. | Mucinex is used for temporary relief of cough and chest congestion caused by common colds, bronchitis, or respiratory infections. |
| Side Effects | Common side effects of Sudafed include nervousness, restlessness, dizziness, headache, and trouble sleeping. It may also cause an increased heart rate or elevated blood pressure, particularly in individuals sensitive to stimulants or those with pre-existing conditions. In rare cases, allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, or difficulty breathing may occur. If these occur, seek medical attention immediately. | Common side effects of Mucinex include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, or an upset stomach, which are usually mild and temporary. In rare cases, it may cause allergic reactions such as rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, or difficulty breathing. If side effects persist, or worsen, or you experience signs of a serious allergic reaction, it is important to discontinue use and seek medical attention. |
| Duration/Course | 4-6 hours | 12 hours |
| Onset | Within 15-30 minutes | Within 15-30 minutes |
| Dosage | Always consult your doctor to determine the appropriate dosage of Sudafed for your specific condition, as the dosage may vary depending on your age, underlying health issues, or other medications you may be taking. | Always consult your doctor to determine the appropriate dosage of Mucinex for your specific condition, as the dosage may vary depending on your age, underlying health issues, or other medications you may be taking. |
| Drug Interaction | Sudafed can interact with certain medications like monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), antihypertensive medications, stimulants, and some antidepressants which may increase the risk of side effects or reduce its effectiveness. Always consult your healthcare provider if you take any of these medications before taking Sudafed. | Stop use and consult your doctor if your cough lasts more than 7 days, comes back, or is accompanied by a fever, rash, or persistent headache. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, consult your healthcare provider before use. |
| Warnings/Precautions | Do not exceed the recommended dosage of Sudafed. If symptoms do not improve within 7 days or if they are accompanied by a fever, discontinue use and consult your healthcare provider. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, seek advice before using this product. | Stop use and consult your doctor if your cough lasts more than 7 days, comes back, or is accompanied by a fever, rash, or persistent headache. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, consult your healthcare provider before use. |
What’s the Best Alternative for Sudafed and Mucinex?
If you're looking for an alternative to Sudafed and Mucinex, Allermi may be the solution. Unlike oral medications, Allermi comes in a nasal spray form and offers a more customized treatment. Since Allermi is a nasal spray and is mainly absorbed by the nose, it does not have the side effects that Sudafed and Mucinex have.
Allermi may offer a better option for some patients who may not be suitable for Sudafed or Mucinex. For example, Sudafed can cause side effects like increased heart rate or high blood pressure, while Mucinex is mainly for chest congestion and may not work as well for nasal symptoms. Side effects with Allermi are rare and usually mild because the medicine mainly goes to the nose and does not spread to the rest of the body. If they occur, they can often be eased by adjusting the formula or technique.
Allermi combines multiple active ingredients, including an antihistamine, micro-dosed decongestant, anti-discharge, and anti-inflammatory. This approach helps relieve symptoms like congestion, inflammation, and sneezing in a way that Sudafed and Mucinex cannot.
When it comes to onset, Allermi is quicker — many users report noticeable symptom improvement within 10-15 minutes of use. Plus, it provides longer-lasting relief, with continued effectiveness over 3-4 weeks of use.
Related: How Long Does It Take for Allergy Medicine to Work?
The Bottom Line
Sudafed helps with nasal congestion, and Mucinex is for chest congestion. However, some people may experience side effects or find that these medications don’t solve all their symptoms.
Allermi is a great alternative. It’s a nasal spray that combines different ingredients to treat both nasal and chest congestion. It works faster, lasts longer, and has fewer side effects, which makes it a better option for many.
References:
- Głowacka, K., & Wiela-Hojeńska, A. (2021). Pseudoephedrine—Benefits and Risks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(10), 5146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105146
- Albrecht, H. H., Dicpinigaitis, P. V., & Guenin, E. P. (2017). Role of guaifenesin in the management of chronic bronchitis and upper respiratory tract infections. Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine, 12, 31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40248-017-0113-4