- Eye allergies can cause itchy, red and watery eyes.
- Common allergens include pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and mold spores.
- Nasal allergies that occur alongside eye allergies need comprehensive allergy care.
Our eyes are constantly exposed to the environment, and they can react to various elements that trigger symptoms like itching, redness, and tearing. These reactions may indicate eye allergy.
If you experience these symptoms at specific times of the year or after certain exposures, you know how bothersome they can be. This article helps you understand eye allergies, their causes, and effective ways to prevent and treat them.
What are Eye Allergies?
Eye allergies, also known as allergic conjunctivitis, are a common condition where the eyes become red, itchy, and irritated due to an immune system overreaction to environmental allergens. These allergens can include pollens, pet dander, and dust mites.
Although eye allergy is an important health concern—as it affects up to 40% of the population—unfortunately, many people with the condition do not seek medical consultation [*].
There are four types of allergic conjunctivitis:
- Simple Allergic Conjunctivitis. This is due to simple allergen exposure on the ocular surface. It can occur alongside other allergic conditions like allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and asthma.
- Seasonal Allergic Conjunctivitis (SAC). Also called "hay fever" this condition may worsen in spring and summer due to tree, grass and weed pollens.
- Perennial Allergic Conjunctivitis (PAC). This occurs year-round. Dust mites, animal dander, and mold spores are known triggers.
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis (VKC). This is a more complex form, believed to result from climate and allergen exposure, involving IgE and immune mechanisms. It’s more prevalent in warm and dry climates [*].
What are the Symptoms of Eye Allergies?
Eye allergies can cause various symptoms, including:
- Redness
- Itching
- Watery eyes
- Burning sensation
- Sensitivity to light
- Grittiness (the sensation that there’s something in the eye)
- Sneezing
These symptoms can vary in intensity depending on the individual and the severity of the allergic reaction.
What Causes Eye Allergies?
Eye allergies are primarily caused by the immune system's overreaction to environmental or airborne allergens that come into contact with the eyes. When the eyes are exposed to allergens, the immune system releases chemicals like histamine to combat what it perceives as a threat.
Common allergens that can trigger eye allergies include:
- Pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds, especially during specific seasons, can trigger allergic reactions.
- Pet dander
- Dust mites
- Mold spores
- Cosmetics or perfumes
- Smoke
How are Eye Allergies Diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, including when they started, their frequency, and any possible triggers. An eye examination may also be performed to examine for signs of redness, irritation, and other physical symptoms of allergy.
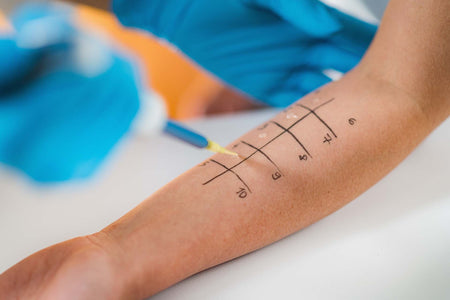
Allergy testing such as skin prick tests or specific IgE blood tests helps to identify the allergens triggering the reaction.
It's important to note that allergic conjunctivitis and other eye conditions can have overlapping symptoms, which is why you need to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
How are Eye Allergies Treated?
Given that eye allergies are influenced by various factors, a single treatment approach may not be sufficient to manage all symptoms. A combination of therapies is often recommended.
Here are some approaches to treating or managing eye allergies:
Avoidance of triggers
It’s important to avoid allergens or minimize your exposure as this helps reduce the frequency and severity of your allergic reactions. You can, for instance, stay indoors and keep your windows closed during high pollen seasons.
Using air purifiers with HEPA filters to reduce indoor allergens like dust mites and pet dander is also a way to minimize exposure.
Additionally, wash your hands and face after going outside, and keep your hands away from your eyes.
Rinsing the eyes with cool water may help after allergen exposure.
Nasal sprays
Though it may not seem obvious, using a nasal spray can play an important role in addressing eye allergy symptoms.
When there is nasal inflammation due to allergies, the eyes can react with itching, redness, and tearing.
By reducing nasal inflammation and inflammation on the duct that leads to the eyes, nasal sprays can have a beneficial effect on allergic eye symptoms.
There are a few different nasal sprays that may help with eye allergies:
- Steroid nasal sprays. These reduce the underlying inflammation in the nasal passages, which makes them a very effective treatment for bothersome allergy symptoms like nasal congestion, runny nose, and itchy, watery eyes. Although they are considered the first-line treatment for allergies, it can take a few weeks of consistent use to experience an improvement in symptoms.
- Antihistamine nasal sprays. These work by blocking the effects of histamine, which is responsible for many allergy symptoms such as itch, sneeze and runny nose. Inhibiting histamine leads to symptom relief—and these sprays work much faster than steroid nasal sprays.
- Combination nasal sprays. Some nasal sprays combine more than one type of medication to treat allergy symptoms more effectively. Allermi, for instance, contains 3-4 active ingredients, including an antihistamine, anti-inflammatory and micro-dosed decongestant, at the right percentages based on an individual’s symptoms.
Eye drops
Eye drops can help manage eye allergies by directly addressing symptoms such as itching and redness, applied directly to the surface of the eye.
There are a few different eye drops for eye allergies:
- Antihistamine eye drops. These work by blocking histamine receptors in the eyes, which reduces itching and inflammation caused by allergens.
- Mast cell stabilizer eye drops. These can prevent the release of histamine and other chemicals that contribute to allergic reactions and are good for achieving longer-term relief.
- Redness-relief eye drops. These can reduce eye redness, although they should be used cautiously and for short durations to avoid rebound effects.
- Lubricating eye drops. These medication-free “artificial tears” can relieve dryness and irritation of the surface of the eye.
Remember to always follow the directions on the label when using eye drops for safety and effectiveness.
Related: Decongestants vs. Antihistamines
Allergy shots
Allergy shots, also known as subcutaneous immunotherapy, can help manage eye allergies by desensitizing the immune system to specific allergens that trigger allergic reactions.
Immunotherapy involves injecting small, gradually increasing amounts of the allergen into the body over time. This process helps the immune system become less sensitive to the allergen.
For those with eye allergies, this intervention can lead to decreased symptoms, including itching and redness of the eyes. These allergy shots may be beneficial if relief from medications hasn’t been achieved.
Related: What to Do When Allergy Medicine Doesn’t Work
How Can I Prevent Eye Allergies?
To prevent eye allergies, consider these strategies at home or when going outdoors:
- Wear sunglasses or glasses to shield your eyes from pollen and other allergens when outdoors.
- Wash your hands frequently, shower, and change clothes, especially after outdoor activities to remove allergens.
- Consider keeping pets out of the bedroom to reduce dander.
- Wipe down surfaces with a damp cloth instead of dry dusting.
- Use allergen-proof covers for pillows and mattresses.
- Vacuum frequently using a HEPA (high-efficiency particulate air) filter.
How Long Do Eye Allergies Last?
The duration of eye allergies can vary depending on the allergen exposure and individual response. It is possible for your symptoms to last if the allergen is still present in the environment or until you receive effective treatment.
The Bottom Line
Eye allergies or allergic conjunctivitis can impact your quality of life by causing discomfort, itching and tearing of the eyes. However, it is possible to reduce your symptoms by limiting exposure to allergens, using the proper medications and consulting a board-certified allergist if symptoms do not improve.
Always consult a medical professional to receive an accurate diagnosis and a personalized plan.
Experiencing nasal allergies alongside eye allergies? It’s important to address symptoms like runny nose, sneezing, and nasal congestion. For effective management of these symptoms, consider Allermi’s comprehensive allergy care.
References:
- Baab, S., Le, P. H., Gurnani, B., & Kinzer, E. E. (2024, January 26). Allergic Conjunctivitis. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448118/
- Kaur, K., & Gurnani, B. (2023, June 11). Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK576433/